Using a System Property to Debug SOAP Messages
<system-properties>
<property name="org.apache.cxf.logging.enabled" value="true"/>
</system-properties>
To include this property in the configuration from the CLI:
/system-property=org.apache.cxf.logging.enabled:add(value=true)
Once that this property has been set to true, you will see in your server logs the SOAP Messages. As an example, here is the incoming SOAP Request:
Address: http://localhost:8090/jaxws-pojo-endpoint/JSEBean
HttpMethod: POST
Content-Type: text/xml;charset=UTF-8
ExchangeId: a6f15ee8-df14-4f1e-9942-36f0475e7bb6
ServiceName: JSEBeanService
PortName: JSEBeanPort
PortTypeName: JSEBean
Headers: {SOAPAction="", User-Agent=Apache-HttpClient/4.1.1 (java 1.5), connection=Keep-Alive, content-type=text/xml;charset=UTF-8, Host=localhost:8090, Content-Length=287, accept-encoding=gzip,deflate}
Payload: <soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" xmlns:jsr="http://jsr181pojo.samples.jaxws.ws.quickstarts.jboss.org/">
<soapenv:Header/>
<soapenv:Body>
<jsr:echo>
<arg0>Hello</arg0>
</jsr:echo>
</soapenv:Body>
</soapenv:Envelope>
And here is the SOAP Response:
INFO [org.apache.cxf.services.JSEBean.RESP_OUT] (default task-1) RESP_OUT
Address: http://localhost:8090/jaxws-pojo-endpoint/JSEBean
Content-Type: text/xml
ResponseCode: 200
ExchangeId: a6f15ee8-df14-4f1e-9942-36f0475e7bb6
ServiceName: JSEBeanService
PortName: JSEBeanPort
PortTypeName: JSEBean
Headers: {}
Payload: <soap:Envelope xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"><soap:Body><ns1:echoResponse xmlns:ns1="http://jsr181pojo.samples.jaxws.ws.quickstarts.jboss.org/"><return>JSEBean pojo: Hello</return></ns1:echoResponse></soap:Body></soap:Envelope>
IMPORTANT: This property is read at server start up. Therefore, you need to restart WildFly to see the effect of this change.
Adding Logging Feature
Features in CXF works like decorators. It can be applied to server and client bus components. In a nutshell it extends the functionality of the server, client or the bus. CXF provides some of the built-in Feature implementations and one of them is LoggingFeature feature class. The LoggingFeature class performs logging of SOAP messages. You can simply add the LoggingFeature to your endpoint as follows:
@org.apache.cxf.feature.Features(features={"org.apache.cxf.feature.LoggingFeature"})
Please note that you can add Features using JaxWsServerFactoryBean as shown in the following code:
HelloWorldImpl implementor = new HelloWorldImpl();
JaxWsServerFactoryBean svrFactory = new JaxWsServerFactoryBean();
svrFactory.setServiceClass(HelloWorld.class);
svrFactory.setAddress("http://localhost:9000/helloWorld");
svrFactory.setServiceBean(implementor);
svrFactory.getFeatures().add(new LoggingFeature());
svrFactory.create();
Using a Proxy to capture SOAP Messages
Another option is to use a proxy which prints the incoming and outgoing SOAP Messages. There are plenty of options available like netcat, For example, here is how to set up a proxy on port 8082 which forwards tcp messages on port 8080, printing them:
ncat -lkv localhost 8082 -c 'tee /dev/stderr | ncat -v localhost 8080 | tee /dev/stderr'
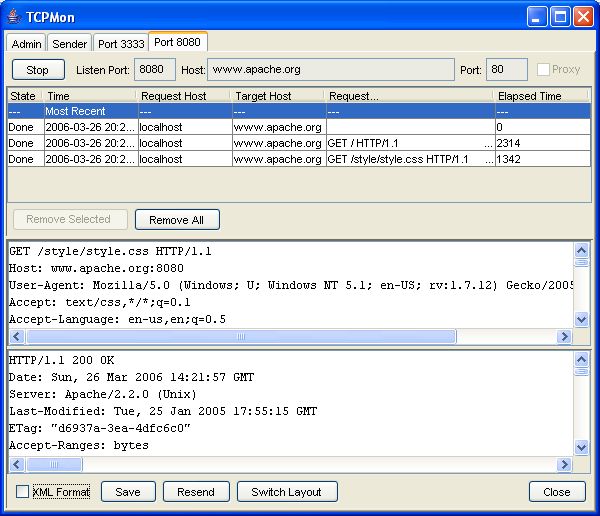
If you prefer using a graphical tool for setting up a proxy, then you can use Apache TCPMon which is a valuable tool for monitoring your network applications.
In the Admin tab select a Listening port for Apache TCPMon and a target port which corresponds to JBoss AS listening port. For example:
Now modify your Web Services client so that they point to the Apache TCPMon Port instead of JBoss. For example:
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception {
String endpointURI ="http://127.0.0.1:8888/ejb/HelloWorld?wsdl";
String helloWorld = "Hello world!";
Object retObj = getPort(endpointURI).echo(helloWorld);
System.out.println(retObj);
}
https://ws.apache.org/tcpmon/tcpmontutorial.html
