This guide contains some tips to teach you how to start, stop, restart WildFly application server. By the end of this tutorial, you will be able to effectively manage the lifecycle of your Wildfly server as needed.
First of all, WildFly can be run in two modes: Standalone mode and Domain mode.
Booting WildFly in Standalone mode
You can start WildFly as follows. Move into the bin folder of your installation and run:
$ ./standalone.sh
The above command will start WildFly with the default (standalone.xml) configuration. If you want to provide another configuration available, just pass it as argument:
$ standalone.sh -c standalone-full.xml
The recommended way to stop WildFly is by connecting to it via its management interface (jboss-cli.sh):
$ ./jboss-cli.sh
Then, from there execute:
[standalone@localhost:9990 /] shutdown
You can restart the application server, passing it as argument to shutdown:
[standalone@localhost:9990 /] shutdown --restart=true
Finally, you can also specify in a timeout for the shutdown as follows
[standalone@localhost:9990 /] shutdown --timeout=10
If there is no timeout specified it will wait indefinitely.
Finally, please notice that you can also issue the shutdown command in non-interactive way. For example:
./jboss-cli.sh -c --commands=":shutdown"
Booting WildFly in Domain mode
You can start WildFly Domain as follows. Move into the bin folder of your installation and run:
$ ./domain.sh
Firstly, the recommended way to stop WildFly is by connecting to it via its management interface (jboss-cli.sh):
$ ./jboss-cli.sh
To Stop all servers in a Host:
/host=master:stop
To restart all servers in a Host:
/host=master:stop(restart=true)
To Stop a single server in a Host:
/host=master/server-config=server-one:stop
Finally, to restart a single server in a Host:
/host=master/server-config=server-one:stop(restart=true)
To learn mode about Domain mode we recommend checking this article: WildFly / JBoss Domain configuration
How to start, stop, restart WildFly when the CLI is not available
If you have a Management user, you can still Start, Stop and Restart WildFly using the Web Console which is available at http://localhost:9990
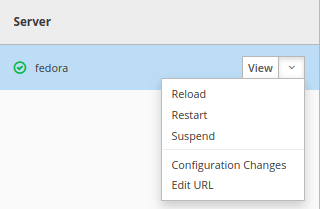
When running in Standalone mode, select the Runtime upper Tab and, from your Server name, click on the Combo Menu’s arrow. You should be able to Reload, Restart or Suspend the Server from there:
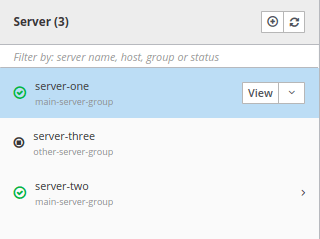
Much the same way, when running in Domain mode, you can perform the same Management actions on your Domain Host, on Server Groups or on Individual Servers:
Managing the lifecycle of WildFly via JMX
Finally, you can also use JMX to manage certain operations such as shutdown or shutdown with restart using JMX.
The simplest way to do that, is to connect to a tool, for example JConsole, and then access the jboss.as:management-root=server MBean. For example, to shutdown the application server:

Besides, you can also operate through the javax.management and perform the shutdown programmatically. For example:
public static void status() throws Exception{
String host = "localhost";
int port = 9990; // management-http port
String urlString = "service:jmx:remote+http://" + host + ":" + port;
System.out.println("\n\n\t**** urlString: "+urlString);;
JMXServiceURL serviceURL = new JMXServiceURL(urlString);
Map map = new HashMap();
String[] credentials = new String[] { "admin", "admin" };
map.put("jmx.remote.credentials", credentials);
JMXConnector jmxConnector = JMXConnectorFactory.connect(serviceURL, map);
MBeanServerConnection connection = jmxConnector.getMBeanServerConnection();
ObjectName mbeanName = new ObjectName("jboss.as:management-root=server");
connection.invoke(mbeanName, "shutdown", null, null);
jmxConnector.close();
}
Conclusion
This article was a walk through a set of options to manage the lifecycle of the application server using different tools (CLI / Web Console / JMX API). You should now be able to manage the lifecycle of the server effectively.
Found the article helpful? if so please follow us on Socials