In Java Persistence API (JPA), the Many-to-Many relationship represents a common scenario where multiple instances of one entity are associated with multiple instances of another entity. This tutorial will guide you through the process of implementing a Many-to-Many relationship using JPA.
What is a Many to Many Relationship?
In a Many-to-Many relationship, entities from both sides of the relationship can be related to multiple instances of the other side. For example, in the following association, a Customer has Many Address and an Address can, in turn, have Many Customer:
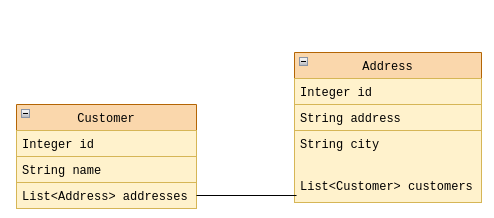
To understand the implications of the Many-to-Many relationship on entity mapping and database schema we will see a practical example using a JPA/Hibernate application.
Coding a sample application
A many-to-many mapping is expressed on both the source and target entities as a @ManyToMany
annotation on the collection attributes. For example, in the following code, the Customer Entity has an addresses attribute that has been annotated with @ManyToMany. Likewise, the Address Entity has a customers attribute that has also been annotated with @ManyToMany:
@Entity
public class Customer implements Serializable {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@NotNull
private String name;
@NotNull
private String email;
@NotNull
@Column(name = "phone_number")
private String phoneNumber;
@ManyToMany(cascade = {CascadeType.PERSIST, CascadeType.MERGE})
private List<Address> addresses = new ArrayList();
// Getters/Setters omitted for brevity
}
Conversely, this is the Address Entity:
@Entity
public class Address implements Serializable {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column
private String street;
@Column
private String city;
@ManyToMany(mappedBy = "addresses")
private List<Customer> customers = new ArrayList();
}
Finally, we will add a simple Stateless Bean to insert some records and fetch a Customer with the related Addresses:
@Stateless
public class ServiceBean {
@PersistenceContext
private EntityManager em;
public String create() {
Customer customer1 = new Customer();
customer1.setName("John Smith");
customer1.setPhoneNumber("328/1145678");
customer1.setEmail("[email protected]");
Customer customer2 = new Customer();
customer2.setName("Frank Smith");
customer2.setPhoneNumber("313/3454643");
customer2.setEmail("[email protected]");
Address address1 = new Address();
address1.setStreet("15th Avenue");
address1.setCity("New York");
Address address2 = new Address();
address2.setStreet("Rue de Rivoli");
address2.setCity("Paris");
List<Address> list1 = new ArrayList();
list1.add(address1);
list1.add(address2);
customer1.setAddresses(list1);
List<Address> list2 = new ArrayList();
list2.add(address1);
customer2.setAddresses(list1);
em.persist(customer1);
em.persist(customer2);
return "Created!";
}
public Customer findCustomer(Long i) {
Customer c = this.em.find(Customer.class, i);
System.out.println("Found Customer "+c);
System.out.println("Found Addresses "+c.getAddresses());
return c;
}
}
To run the above example using the default H2 Datasource, you can include in your persistence.xml the following persistence unit:
<persistence-unit name="primary">
<jta-data-source>java:jboss/datasources/ExampleDS</jta-data-source>
<properties>
<!-- Properties for Hibernate -->
<property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto" value="create-drop" />
<property name="hibernate.show_sql" value="true" />
</properties>
</persistence-unit>
Conclusion
In this example we have learnt how to code a many-to-many relation with Hibernate/JPA and added a simple Bean to test it.
Source code for this example: https://github.com/fmarchioni/mastertheboss/tree/master/hibernate/ManyToMany
Found the article helpful? if so please follow us on Socials