Please note, this article has been written for JBoss AS 5 so the content might not be suitable for the latest version of the application server. For WildFly users, we recommend checking this article: SOAP Web services on WildFly made simple
JBoss AS 5 ships with Apache CXF web services implementation. In this tutorial we will show how to create a simple Web service endpoint and how to deploy and test it with a client.
Apache CXF is an open source services framework. CXF helps you build and develop services using frontend programming APIs, like JAX-WS and JAX-RS. These services can speak a variety of protocols such as SOAP, XML/HTTP, RESTful HTTP, or CORBA and work over a variety of transports such as HTTP, JMS or JBI.
Developing the Web service
Firstly, create a new Web Project from your IDE.
Then, we will add at first the Web services an interface which will be used by our implementation.
package com.sample;
import javax.jws.WebMethod;
import javax.jws.WebService;
@WebService
public interface Math {
@WebMethod
public long sum(long a, long b);
}
Next, this is the implementation class:
package com.sample;
import javax.jws.WebMethod;
import javax.jws.WebService;
@WebService(endpointInterface = "com.sample.Math", serviceName = "MathWS")
public class MathWS implements Math
{
public long sum(long a, long b) {
System.out.println("Summing "+a+" + "+b);
return a+b;
}
}
Now it’s time to register your Web service. Add your web service in web.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app version="2.5" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd"> <servlet> <servlet-name>MathWS</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.sample.MathWS</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>MathWS</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
A JAX-WS Endpoint can be also configured using Spring XML file in addition to using the JAX-WS APIs. Once you’ve created your server implementation, you simply need to provide the class name and an address.
Here’s a sample jbossws-cxf.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:jaxws="http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/jaxws.xsd"> <!-- one or more jaxws:endpoint POJO declarations --> <jaxws:endpoint id="MathWS" address="http://localhost:8080/Samplews" implementor="com.sample.MathWS"> <jaxws:invoker> <bean class="org.jboss.wsf.stack.cxf.InvokerJSE"/> </jaxws:invoker> </jaxws:endpoint> </beans>
For more details about configuring Apache CXF web services with Apache CXF configuration file, please refer to http://community.jboss.org/wiki/JBossWS-StackCXFUserGuide
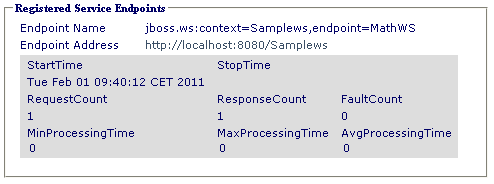
Deploy the service. If everything compiled correctly, you should see in the list of the deployed services your mathWS service.
Point the browser at http://localhost:8080/jbossws/services and check it.
Develop a CXF client.
Here’s a minimal client implementation:
package com.sample;
import org.apache.cxf.interceptor.*;
import org.apache.cxf.jaxws.JaxWsProxyFactoryBean;
public class Client {
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception {
JaxWsProxyFactoryBean factory = new JaxWsProxyFactoryBean();
factory.getInInterceptors().add(new LoggingInInterceptor());
factory.getOutInterceptors().add(new LoggingOutInterceptor());
factory.setServiceClass(Math.class);
factory.setAddress("http://localhost:8080/Samplews");
Math client = (Math) factory.create();
System.out.println("Server said: " + client.sum(3,4));
}
}
Notice the use of JaxWsProxyFactoryBean which is a factory for creating JAX-WS proxies. This class provides access to the internal properties used to set-up proxies. Using it provides more control than the standard JAX-WS APIs.
Found the article helpful? if so please follow us on Socials