In this article, we will dive deep into the world of JMX metrics collection using Byteman, a powerful Java agent, and explore how it can help your monitoring and optimization efforts. Whether you are a seasoned developer or an operations professional, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to unlock the full potential of your application. Let’s embark on this journey to harness the power of JMX metrics with Byteman and take your monitoring to new heights.
If you are new to Byteman I’d suggest reading the Base Documentation and the following tutorials we have published:
An example: how to monitor HTTP Sessions via JMX
To demonstrate how to monitor JMX Attributes, we will show how to monitor the number of HTTP Sessions which are active.
The first step is to create a WebListener that will keep track of the HTTP Session count:
package com.sample;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionListener;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionEvent;
@WebListener
public class SessionCounter implements HttpSessionListener {
private int activeSessions = 0;
public void sessionCreated(HttpSessionEvent se) {
activeSessions++;
}
public void sessionDestroyed(HttpSessionEvent se) {
if (activeSessions > 0) {
activeSessions--;
}
}
public int getActiveSessions() {
return activeSessions;
}
}
In order to collect the value of activeSession we will create an Helper class named JMXHelper that extends the org.jboss.byteman.rule.helper.Helper class. The base Helper class is responsible for handling a Byteman Rule file, providing the base syntax of it.
In our case, we will need additional functionalities as we want to publish an MBean, with the activeSessions, via JMX. Here is our JMXHelper class:
package org.jboss.byteman.sample.helper;
import org.jboss.byteman.rule.Rule;
import org.jboss.byteman.rule.helper.Helper;
import javax.management.MBeanServer;
import javax.management.ObjectName;
import java.lang.management.ManagementFactory;
import javax.management.StandardMBean;
public class JMXHelper extends Helper {
static Data user = new Data("activeCount", 1);
private static boolean DEBUG;
public static void activated() {
DEBUG = Boolean.getBoolean("org.jboss.byteman.sample.helper.debug");
if (DEBUG) {
System.err.println("JMXHelper activated");
}
}
public static void installed(Rule rule) {
if (DEBUG) {
System.err.println("JMXHelper installed, " + rule);
}
}
protected JMXHelper(Rule rule) {
super(rule);
}
public void registerHelperMBean(String name) {
MBeanServer mbs = ManagementFactory.getPlatformMBeanServer();
synchronized (this) {
try {
ObjectName oname = new ObjectName(name);
if (mbs.isRegistered(oname) == false) {
StandardMBean mbean = new StandardMBean(user, DataMBean.class);
mbs.registerMBean(mbean, oname);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public void traceToJMX(int active) {
user.setValue(active);
System.out.println("Number of Active Sessions: " + active);
}
}
The method which is responsible for registering the MBean is registerHelperMBean which requires to be invoked at Server start. The other method is traceToJMX which merely sets the MBean attribute which will be passed from our Rule. Within the Helper class we referenced a Java Bean named DataMBean which is an ordinary Java Bean, fit to be used as StandardMBean:
package org.jboss.byteman.sample.helper;
public interface DataMBean {
public int getValue();
public void setValue(int value);
public String getAttribute();
public void setAttribute(String attribute);
}
Now we will code our rule file- we will name it session.btm:
RULE Register Helper mbean
CLASS org.jboss.modules.Main
METHOD main
HELPER org.jboss.byteman.sample.helper.JMXHelper
AT EXIT
IF TRUE
DO registerHelperMBean("org.jboss.byteman:helper=JMXHelper")
ENDRULE
RULE Count Active Sessions
CLASS com.sample.SessionCounter
HELPER org.jboss.byteman.sample.helper.JMXHelper
METHOD sessionCreated(HttpSessionEvent)
AT EXIT
BIND count:int = $0.getActiveSessions();
IF true
DO traceln("Session count "+count);
traceToJMX(count);
ENDRULE
The first rule is used to register our MBean class through the JMXHelper. It fires when the application server starts.
The second rule is activated when the method sessionCreated of the SessionCounter class exits. At this point the number of activeSession is stored in the Rule variable named count and passed to the JMXHelper which will eventually update the MBean.
Installing the Rule on the JVM
In order to run this Rule, you have to provide to the JAVA_OPTS the path to the Rule file and to the Helper class, which was packaged in a JAR file named Helper.jar and placed in /home/jboss/dist/ .
JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -Dorg.jboss.byteman.transform.all -javaagent:/home/jboss/byteman-download-3.0.3/lib/byteman.jar=script:/home/jboss/byteman-download-3.0.3/sample/scripts/session.btm,boot:/home/jboss/dist/ByteHelper.jar,boot:/home/jboss/byteman-download-3.0.3/lib/byteman.jar"
Update the above shell with the path to your files. Now start the application server and deploy the Web application which contains the SessionCounter class. You should be able to see on the Console, as soon as you invoke some JSP files:
INFO [stdout] (default task-49) Number of Active HTTP Sessions: 2
Monitoring your JMX Metrics
Hint: If you are experiencing issues in firing your rules, include as well the -Dorg.jboss.byteman.verbose in the JAVA_OPTS
Now open JConsole (or any other tool which is able to inspect the MBeans on the application server) and verify that the attribute is correctly updated in the MBean tree:
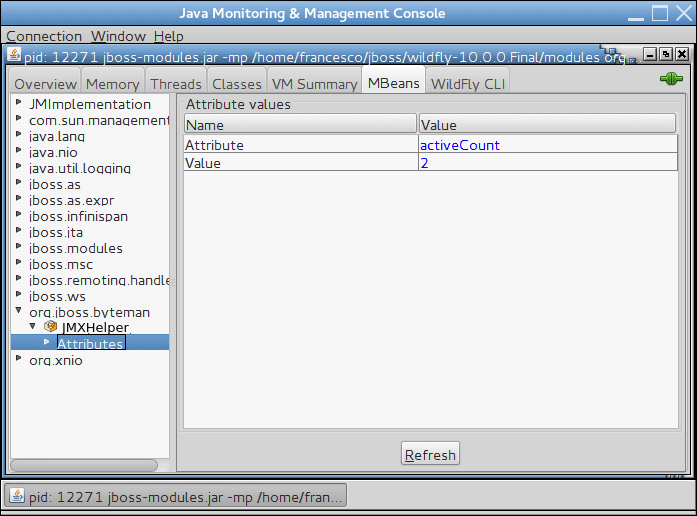
Conclusion
In conclusion, harnessing JMX metrics with Byteman empowers you to monitor and optimize your application like never before. We have explored a specific use case – monitoring the number of active HTTP sessions – to demonstrate the potential of this powerful combination. By leveraging Byteman’s flexibility and JMX’s rich monitoring capabilities, you can gain real-time insights into your application’s session management and make data-driven optimizations. Empowered with this knowledge, you can proactively identify and resolve bottlenecks, enhance scalability, and deliver a seamless user experience.
Found the article helpful? if so please follow us on Socials