Red Hat OpenShift Local (formerly Red Hat Code Ready Containers ) provide a minimal, preconfigured OpenShift 4.X single node cluster to your laptop/desktop computer for development and testing purposes. In this tutorial, we will learn how to set up an OpenShift clusters using with Red Hat OpenShift Local to emulate the cloud development environment on your laptop.
Installing Red Hat OpenShift Local
Red Hat OpenShift Local uses a single node, which behaves as both a control plane and worker node. In this section we will cover the Linux installation. You can refer to the quickstart guide for information about the other OS.
On Linux, Red Hat OpenShift Local requires the libvirt and NetworkManager packages.
You can install them as follows in Fedora/RHEL distributions:
$ sudo dnf install qemu-kvm libvirt NetworkManager
On Debian and Ubuntu, you need to install the following packages:
sudo apt install qemu-kvm libvirt-daemon libvirt-daemon-system network-manager
Next, download the latest release of Red Hat OpenShift Local at: https://console.redhat.com/openshift/create/local
Finally, from the same page download the Pull Secret which you will need during the installation . The Pull Secret is related to your Red Hat account, therefore you need one to complete the installation process
Once downloaded, create a folder named `.crc` in your home directory:
$ mkdir $HOME/.crc
Then unzip the CRC archive in that location:
$ tar -xf crc-linux-amd64.tar.xz -C $HOME/.crc
Next, add it to your system PATH:
PATH="$HOME/.crc/crc-linux-2.23.0-amd64:$PATH" export PATH
Verify that the crc binary is now available:
$ crc version CRC version: 2.23.0+ddcfe8 OpenShift version: 4.13.3 Podman version: 4.4.4
Great, your environment is ready. It’s time to start it!
Starting Openshift cluster
The `crc setup` command will download the OpenShift bundle to your machine:
crc setup
The above step will require some time depending on the speed of your network.
After the download is complete, we recommend setting up an higher Memory Requirement for your OpenShift cluster in order to run Enterprise applications with it (the default is 9 GB):
crc config set memory 16000
The above command will set the Amount of Memory of the OpenShift cluster to 16GB.
Next, you can start the Red Hat OpenShift Local cluster with:
$ crc start
You need to provide the Pull Secret that you have previously downloaded.
Then, the local OpenShift cluster will start:
INFO Checking if oc binary is cached INFO Checking if running as non-root INFO Checking if Virtualization is enabled INFO Checking if KVM is enabled INFO Checking if libvirt is installed INFO Checking if user is part of libvirt group INFO Checking if libvirt is enabled INFO Checking if libvirt daemon is running INFO Checking if a supported libvirt version is installed INFO Checking if crc-driver-libvirt is installed INFO Checking if libvirt 'crc' network is available INFO Checking if libvirt 'crc' network is active INFO Checking if NetworkManager is installed INFO Checking if NetworkManager service is running INFO Checking if /etc/NetworkManager/conf.d/crc-nm-dnsmasq.conf exists INFO Checking if /etc/NetworkManager/dnsmasq.d/crc.conf exists INFO Starting CodeReady Containers VM for OpenShift 4.3.0... INFO Verifying validity of the cluster certificates ... INFO Check internal and public DNS query ... INFO Check DNS query from host ... INFO Starting OpenShift cluster ... [waiting 3m] INFO INFO To access the cluster, first set up your environment by following 'crc oc-env' instructions INFO Then you can access it by running 'oc login -u developer -p developer https://api.crc.testing:6443' INFO To login as an admin, run 'oc login -u kubeadmin -p 7z6T5-qmTth-oxaoD-p3xQF https://api.crc.testing:6443' INFO INFO You can now run 'crc console' and use these credentials to access the OpenShift web console Started the OpenShift cluster
So, out of the box, two users have been created for you. An admin user (kubeadmin) and a developer user. Their credentials are displayed in the above log.
Now reach the Web console of OpenShift with:
crc console
You will notice that the connection is insecure as no certificate is associated with that address. Choose to add an Exception in your browser and continue.
After you have entered the username and password, you will be redirected to the Dashboard of Openshift, which features the default project:
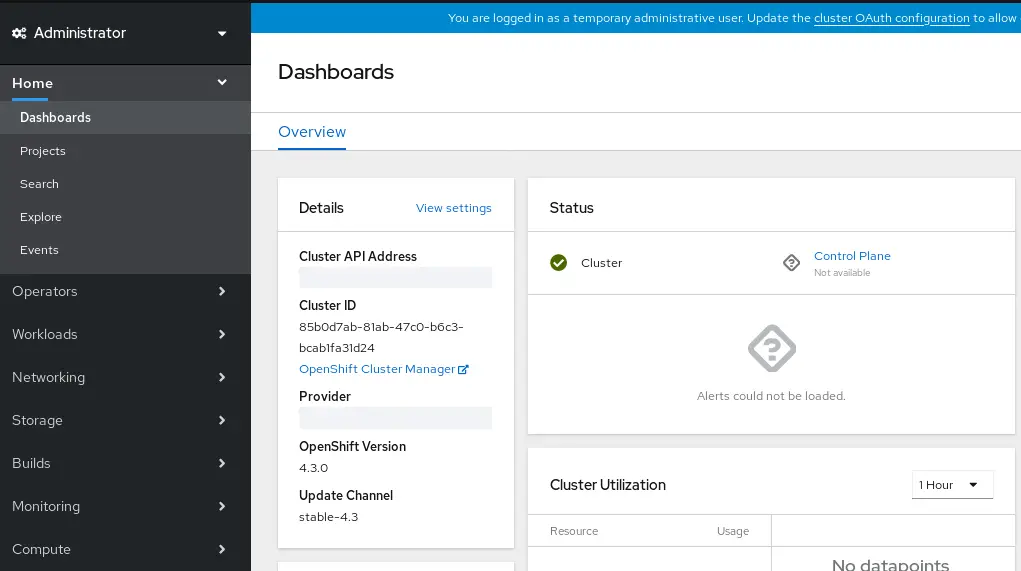
Troubleshooting CRC installation
Depending on your DNS/Network settings, there can be some things that can possibly go wrong.
Let’s start from this error message:
Failed to query DNS from host: lookup api.crc.testing: no such host
This issue is caused by a misconfiguration of your DNS in the file /etc/resolv.conf. Check that it contains the following entries:
search redhat.com nameserver 127.0.0.1
Another common issue is the following one:
CRC - Cannot SSH to VM, crc start failed
The most likely cause is a misconfiguration of your virtual network. You can fix it by releasing any resources currently in use by it and re-creating through the `crc set up`. Here is the script to perform this tasks:
crc stop crc delete sudo virsh undefine crc --remove-all-storage sudo virsh net-destroy crc sudo rm -f /etc/NetworkManager/conf.d/crc-nm-dnsmasq.conf /etc/NetworkManager/dnsmasq.d/crc.conf crc setup crc start
More details about this are available here: https://github.com/code-ready/crc/issues/711
In general terms, if you find an issue with your CRC cluster, it is bes to start crc in debug mode to collect logs with:
crc start --log-level debug
Finally, if you try to upgrade your OpenShift Local Cluster, you might get the following error message:
operation failed: domain 'crc' already exists
This error happens if you have only removed the .crc folder from your machine without destroying/undefining your installation. To safely remove your current installation of OpenShift Local Cluster, after removing the content of the .crc folder also execute:
sudo virsh destroy crc sudo virsh undefine crc
Conclusion
In conclusion, installing and troubleshooting Red Hat OpenShift Local on your laptop can greatly enhance your development workflow, enabling you to efficiently build and test containerized applications right on your local machine. Throughout this article, we’ve covered the step-by-step installation process, ensuring that you have all the necessary dependencies in place and are ready to work seamlessly with Red Hat’s robust container ecosystem.
By utilizing Red Hat OpenShift Local, you gain access to a user-friendly and isolated development environment, equipped with the latest OpenShift features and capabilities. This empowers developers to experiment, iterate, and innovate more effectively, reducing the time spent setting up complex infrastructure and allowing you to focus on what truly matters – delivering high-quality applications.
Found the article helpful? if so please follow us on Socials